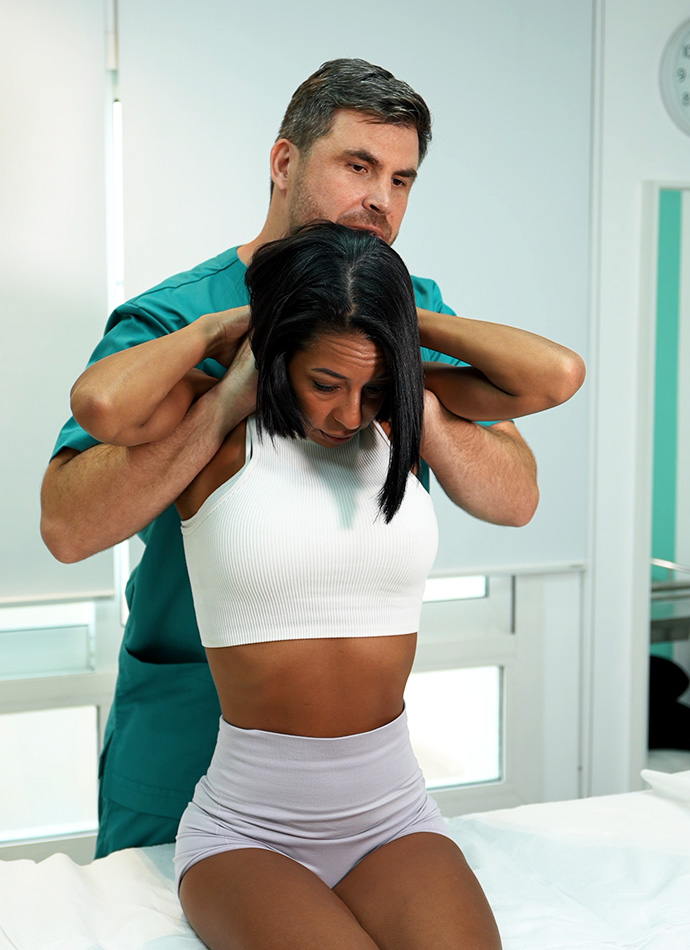
Migraine Clinic Dubai
Migraine is a neurological disorder that manifests itself in an intense or severe headache, which makes it an extremely disabling disease for people who suffer from it.
It affects the frontal part or the entire area of the skull and appears in the form of attacks. It may be accompanied by other symptoms. These attacks can present themselves in the following ways: 1. episodic. When the pain appears up to 9 days a month, we will speak of infrequent episodic attacks; or very frequent episodic if there is pain between 10 and 14 days a month. 2. Chronic: When there are 15 or more problem days per month.
At Physiowell physiotherapy, migraine treatment often involves addressing postural dysfunctions and muscular imbalances in the neck and spine—factors that can also contribute to chronic back issues. Many patients searching for relief from both headaches and tension-related discomfort benefit from complementary services like a back pain massage near me, which supports the clinic’s holistic approach to long-term wellness.
What are the Types of Migraine?
1. Migraine without aura
It causes severe pain, which interferes with normal activity, and its main symptoms are: Pain on one side of the head, although in some cases it can spread throughout the head. In some cases, it is a throbbing pain (the heartbeat is felt). Less commonly, the pain may be felt as neck pain or may extend to the jaw. The pain appears spontaneously and usually lasts more than 4 hours and less than 3 days. In children and teenagers, attacks can last less than 4 hours.
2. Migraine with aura
It is distinguished from migraine without aura by the appearance of other symptoms (aura), which can affect different senses: sight, touch, and/or language. These symptoms often precede the pain and, less frequently, may appear during or after the pain.
Conditions Treated

